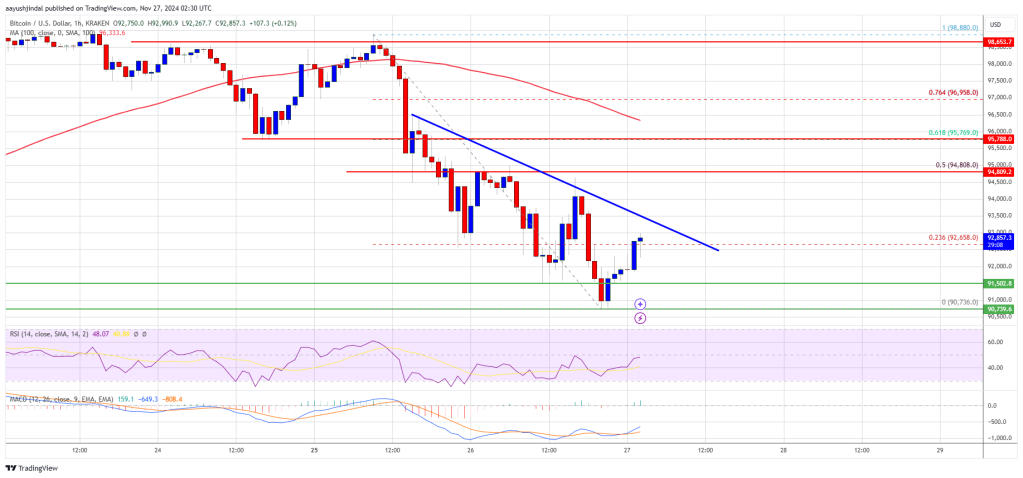
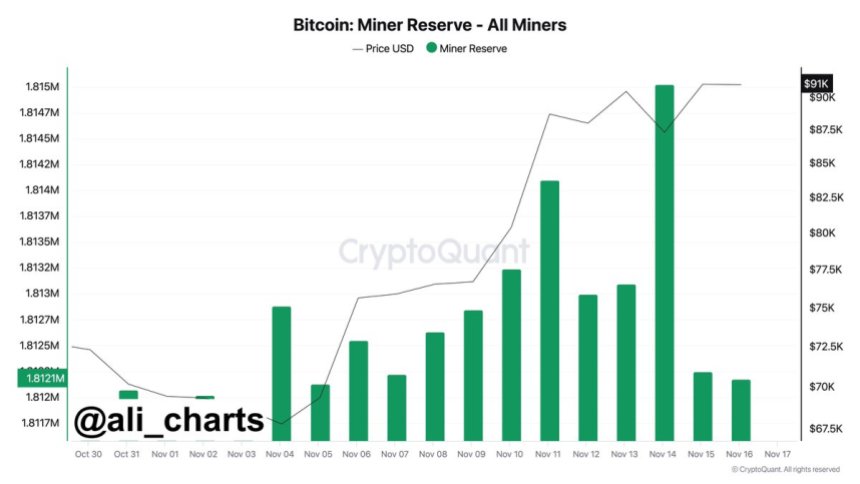
Bitcoin prices have been stagnant, trading below the psychological $30,000 level. The coin is technically under pressure, declining from its peaks of around $31,800 recorded in early July 2023. Amid this development, on-chain data reveals that the Bitcoin miner reserve has been increasing, notwithstanding prevailing market conditions, bouncing back from May 2023 lows. According to data from CryptoQuant, the BTC miner reserve stands at 1.841 million as of July 30, up from 1.826 million on May 27.
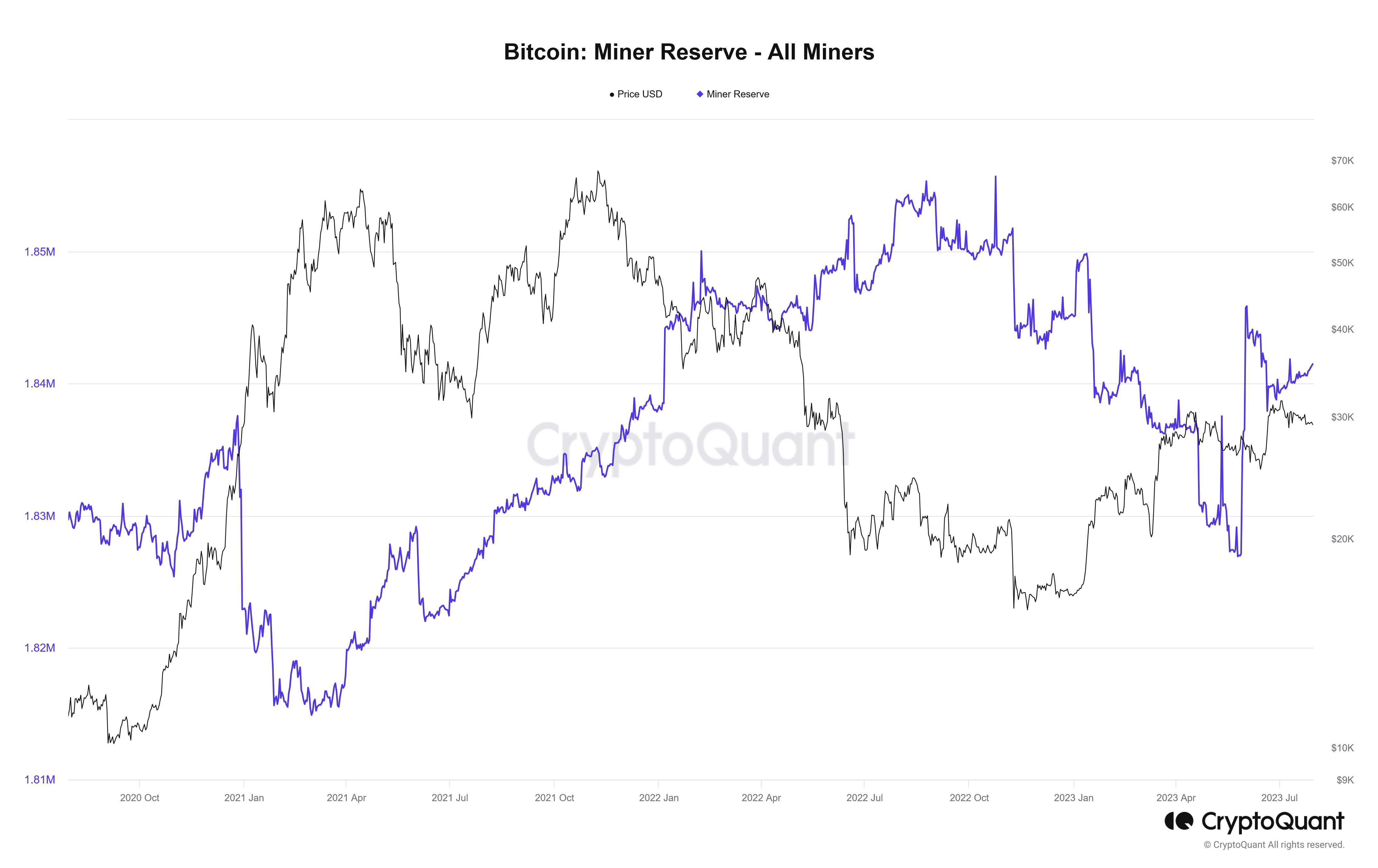
The increasing BTC miner reserve and relatively stable and steady coin prices suggest a sense of optimism among miners. This could improve sentiment and confidence among miners, possibly boosting prices and preventing sellers from pressing the coin even lower. Presently, as mentioned earlier, BTC is trending below $30,000.

In crypto, the Bitcoin miner reserve measures all BTC in the hands of all miners and mining pools. It shows the total number of BTC that is yet to be liquidated. Price-wise, this is important. Miners frequently sell their coins to cover operational costs and realize profits. Therefore, trackers often monitor their trading patterns for valuable insights into market sentiment.
Bitcoin miner reserve trends are important for traders. However, other critical factors could influence prices in future sessions, some of which might have adverse effects. One key consideration is how different countries decide to regulate cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin, as their move can impact liquidity and investor perception.
In the United States, for instance, the approval or rejection of a Bitcoin Spot ETF by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) could significantly affect Bitcoin’s price in the months ahead. The approval of a Bitcoin ETF would enable institutional players to include Bitcoin in their portfolios, injecting capital into the crypto markets and potentially increasing liquidity. Currently, Grayscale’s GBTC, a close-ended trust, allows institutions to get exposure to Bitcoin without directly buying BTC.
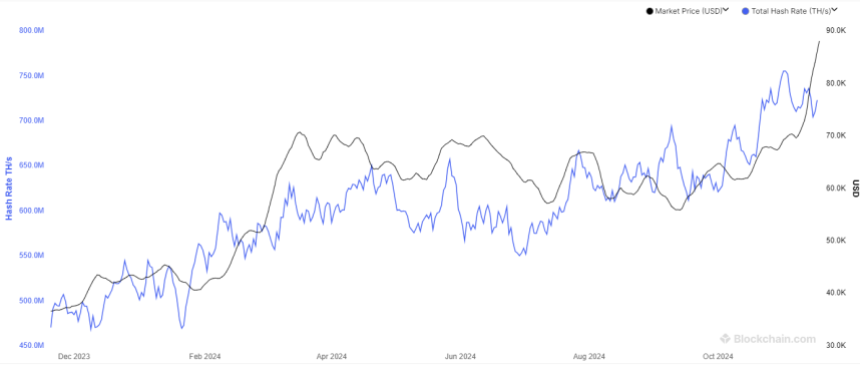
Beyond price-related factors, Bitcoin’s proof-of-work network has faced criticism for its substantial energy consumption to power its operations. In response to environmental concerns, China banned Bitcoin and crypto mining activities, resulting in a drop in the network’s hash rate and negatively impacting BTC prices. Whether the US and Europe will follow a similar path in the future could also have implications for Bitcoin’s price trajectory.

Bitcoin Miner Reserve Rising
The increasing BTC miner reserve and relatively stable and steady coin prices suggest a sense of optimism among miners. This could improve sentiment and confidence among miners, possibly boosting prices and preventing sellers from pressing the coin even lower. Presently, as mentioned earlier, BTC is trending below $30,000.
In crypto, the Bitcoin miner reserve measures all BTC in the hands of all miners and mining pools. It shows the total number of BTC that is yet to be liquidated. Price-wise, this is important. Miners frequently sell their coins to cover operational costs and realize profits. Therefore, trackers often monitor their trading patterns for valuable insights into market sentiment.
Bitcoin miner reserve trends are important for traders. However, other critical factors could influence prices in future sessions, some of which might have adverse effects. One key consideration is how different countries decide to regulate cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin, as their move can impact liquidity and investor perception.
Regulation, Energy Consumption Criticism Negative For Prices
In the United States, for instance, the approval or rejection of a Bitcoin Spot ETF by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) could significantly affect Bitcoin’s price in the months ahead. The approval of a Bitcoin ETF would enable institutional players to include Bitcoin in their portfolios, injecting capital into the crypto markets and potentially increasing liquidity. Currently, Grayscale’s GBTC, a close-ended trust, allows institutions to get exposure to Bitcoin without directly buying BTC.
Beyond price-related factors, Bitcoin’s proof-of-work network has faced criticism for its substantial energy consumption to power its operations. In response to environmental concerns, China banned Bitcoin and crypto mining activities, resulting in a drop in the network’s hash rate and negatively impacting BTC prices. Whether the US and Europe will follow a similar path in the future could also have implications for Bitcoin’s price trajectory.